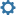
Tephrosia purpurea is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae. It grows in poor soils as a common wasteland weed and has a pantropical distribution. It is a type of legume native to south-western Asia (the Levant, Arabian Peninsula, Socotra, Iran, Pakistan, India and Sri Lanka) and north-eastern Africa (Egypt, Sudan, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Djibouti, Somalia).
The leaflets of the plant are obovate-oblong and equal-sided, and of a silky texture. The fruits (legumes) are typically 1 to 2 in (25 to 51 mm) long and contain six or seven brownish seeds. The species typically grows in areas where the soils are relatively deep, especially in semi-arid and wadi areas, and on terraces and slight inclines and hills.
Tephrosia purpurea is known to be toxic to goats. Although it has been used in Oman and the United Arab Emirates to treat bronchitis, cough, earache, nasal congestion and wounds and bone fractures, as of 1993 its wider impact on humans had not been assessed. It can be used to make indigo-like dyes, and the leaves and those of other plants are used to make hot drinks by the Bedouin in parts of Sinai and the Negev.
![(Tephrosia purpurea subsp leptostachya - OM0659) {} [ ] No Rights Reserved (Tephrosia purpurea subsp leptostachya - OM0659) @11 [ ] No Rights Reserved Unspecified Unspecified](https://991546.shichuantrade-tw.tech/pics/_w70/SAFH/OM0659%2B1319473938.jpg)